
Amirreza Azad
PhD Candidate
Multiscale Modeling of Bubble Evolution on Nano-Structured Electrodes
email: amirreza.azad@mail.utoronto.ca
Biosketch
Amirreza Azad is a PhD student at the Mechanical & Industrial Engineering (MIE) Department, University of Toronto, specializing in the computational modeling of clean energy systems. Amirreza graduated with honors from the University of Tehran, earning Bachelor’s and Master’s degrees in Mechanical Engineering. His strong foundation in Fluid Mechanics, Thermodynamics, and Heat Transfer has been instrumental in advancing his current research, which centers on using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations integrated with Machine Learning techniques to optimize hydrogen electrolysis and carbon capture systems.
Research
Amirreza’s research employs a comprehensive and systematic approach to investigate bubble dynamics on gas-evolving electrodes, aiming to optimize electrochemical processes. The methodology is structured in several stages to address key aspects of bubble nucleation, multiple bubble growth from nanoscale to microscale, and subsequent machine learning-based prediction of bubble distribution at microscale. The proposed steps for this work are shown in Figure 1.
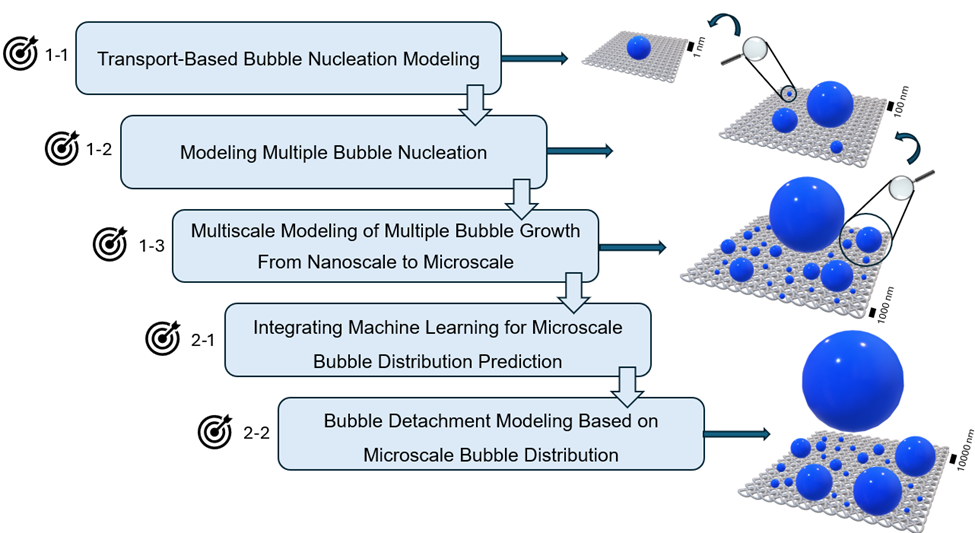
Figure 1: The proposed steps for multiscale modeling of bubble dynamics on a gas-evolving electrode
The first stage will model single-bubble nucleation, examining how the electric field, surface properties, ion transport, and gas diffusion affect gas concentration across the electrode-electrolyte interface, particularly within nanoscale surface cavities. This analysis will incorporate transport-based contributions to multiple bubble nucleation, which will be addressed in the second stage. The third stage will develop a multiscale model to simulate bubble growth from nanoscale nucleation to microscale distribution, capturing transitions, growth, and bubble coalescence. This model will reveal the impact of surface wettability, nanoscale bubble blockage, and microscale bubble interactions on further nucleation. The fourth stage will address coupling nanoscale bubble growth to microscale bubble distribution to accelerate simulation by balancing time steps (Machine Learning architecture is shown in Figure 2). Finally, the fifth stage will apply Volume of Fluid (VOF) modeling to estimate microscale bubble distribution.
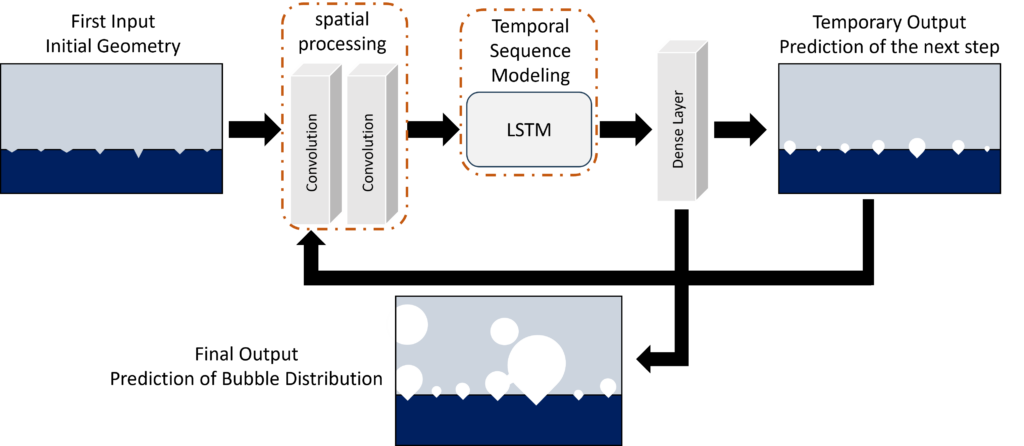
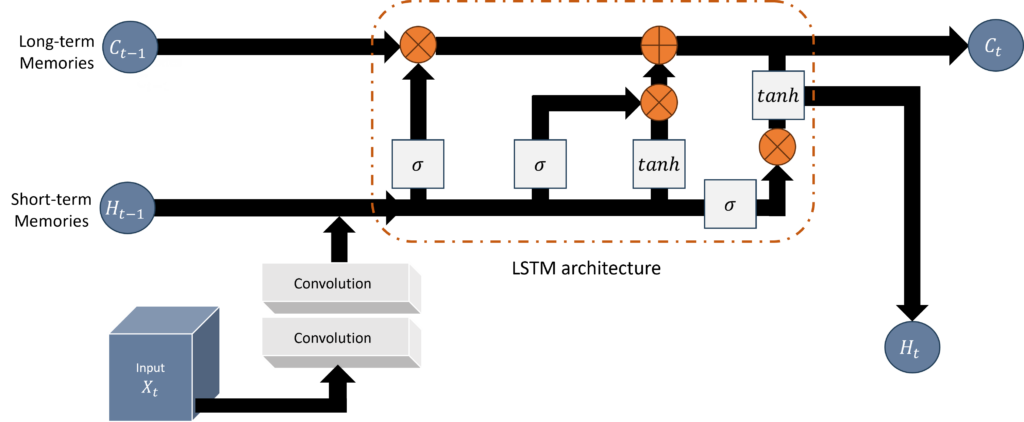
Figure 2: Machine Learning integration for prediction of microscale bubble distribution
